Selank has emerged as a promising peptide therapy, attracting attention for potential cognitive benefits, especially in the context of aging and neurodegeneration. This article presents a comprehensive, evidence-based exploration from human studies, examining its mechanisms, safety profile, and practical relevance to cognitive health in older adults.

Introduction to Selank
Aging populations are experiencing an increased burden of cognitive decline—ranging from subtle memory lapses to debilitating neurodegenerative diseases. As traditional pharmacological options often fall short in effectiveness or come with substantial side effects, interest in peptide-based interventions has grown. Selank, originally developed in Russia, offers a novel approach to cognitive peptide therapy, touted for its anxiolytic, neuroprotective, and nootropic properties.
What Is Selank?
Selank is a synthetic heptapeptide derived from tuftsin, a natural immunomodulatory peptide. Its unique mechanism affects both neurotransmitter pathways and immune modulation, setting it apart from conventional nootropics. It is administered intranasally, allowing for rapid central nervous system penetration.
Mechanisms of Action: How Does Selank Work?
Selank’s multifaceted action is attributed to:
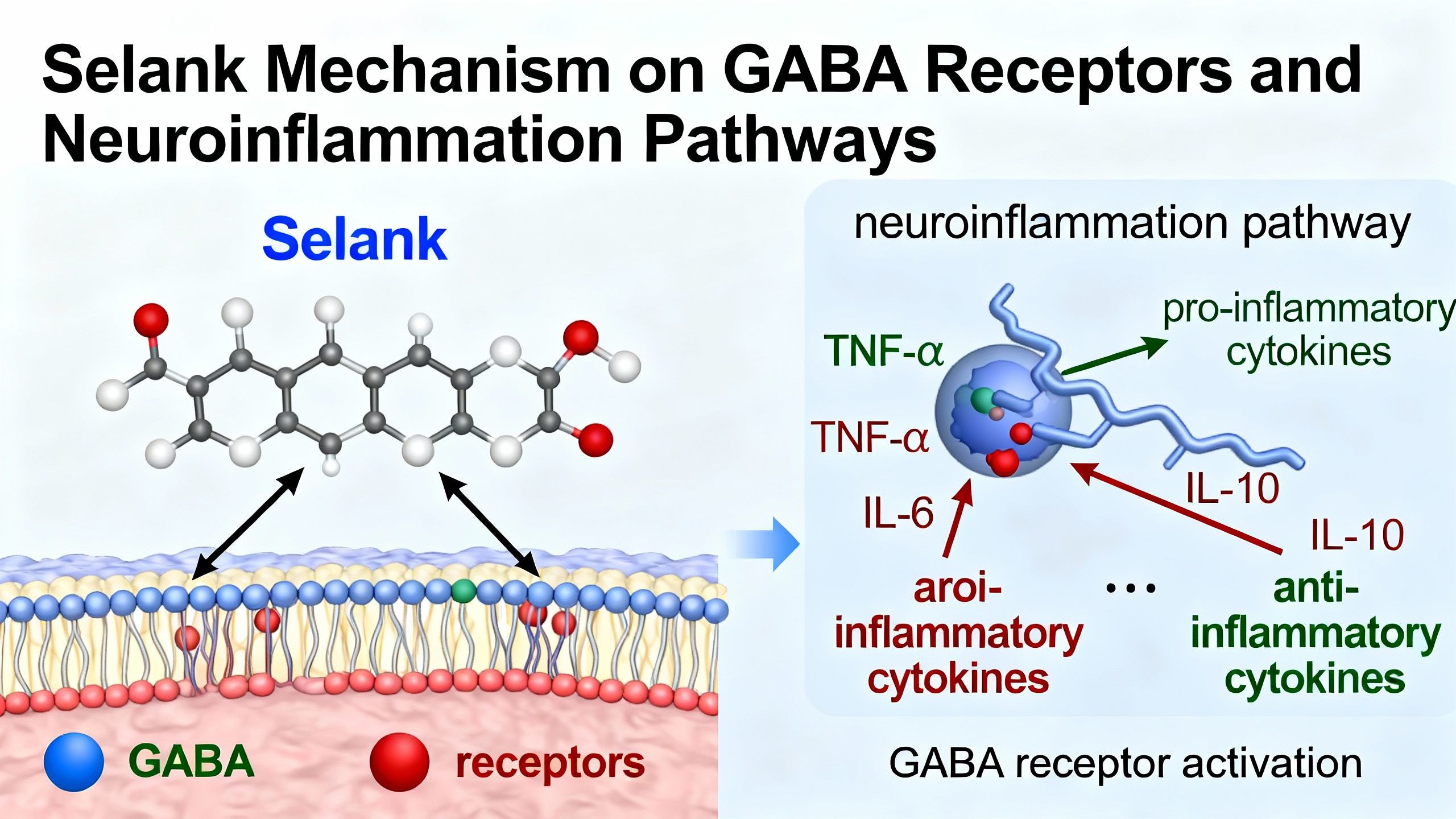
- Modulation of GABAergic transmission, resulting in anxiolytic effects with minimal sedation
- Inhibition of enkephalin-degrading enzymes, prolonging the activity of endogenous opioids
- Promotion of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) expression, supporting neuronal resilience and plasticity
- Anti-inflammatory effects via regulation of cytokine balance, potentially relevant in neuroprotection
This unique interplay makes it an intriguing candidate for cognitive support in aging and neuroprotection strategies.
Selank in Human Studies: Evidence Overview
Although Selank’s research is relatively nascent outside of the Russian Federation, several human trials have provided insight into its clinical relevance.
Cognitive Support
Selank has been investigated for its role in enhancing attention, memory, and learning—key domains that decline with age. Some studies report:
- Improved working memory and recall in older adults
- Enhanced performance on focus-intensive cognitive tasks
- Reduction in symptoms of mild cognitive impairment
Anxiolytic Effects
Aging is frequently associated with increased anxiety and stress reactivity, both of which exacerbate cognitive deterioration.
- Selank demonstrates significant anxiolytic activity in human trials
- Notably, its calming effect is achieved without notable sedation or cognitive dulling, an important distinction from common anxiolytics
Immunomodulation and Neuroprotection
Neuroinflammation is a critical driver of cognitive aging. Early human data suggest:
- Selank can balance pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines
- This immune-modulatory profile may contribute to its neuroprotective properties, reducing risk of progression in neurodegenerative conditions
Selank for Aging: Clinical Applications and Considerations
Selank aging research focuses on preventing cognitive decline and managing stress-induced cognitive impairments. Key points:
- For seniors and at-risk adults: It may help support cognition, especially in those experiencing heightened stress or early-memory complaints
- Cognitive peptide therapy: It stands out because of its dual mechanism and limited side effects compared to traditional therapies
- Individual variability: As with most peptide treatments, the degree of cognitive improvement, speed of effect, and tolerability can differ widely between individuals
Table: Selank’s Potential Benefits in Aging Populations
| Benefit | Human Evidence | Practical Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Anxiety Reduction | Moderate, short-to-mid term | Rapid onset, less sedation than benzodiazepines |
| Memory and Focus Enhancement | Preliminary, limited trials | Subtle improvement in mild impairment |
| Neuroprotection | Early, indirect markers | More research in neurodegenerative cohorts needed |
| Anti-fatigue | Preliminary observations | Subjective energy increase reported |
Safety, Side Effects, and Long-Term Use
Selank is generally regarded as safe in human studies, but long-term outcomes are still being monitored. Key findings:
- Adverse effects are uncommon and rarely severe, most often limited to mild nasal irritation
- No evidence of dependence, withdrawal, or tolerance detected
- No significant drug interactions have been reported in available human trials
- Occasional reports of mild transient headache or gastrointestinal discomfort
- Safety in multimorbid elderly populations remains to be established
Caveat: While Selank’s safety profile is favorable in short-to-medium term studies, absence of comprehensive, long-term, and multinational data warrants caution in routine clinical use outside research settings.
Practical Application: Who Might Benefit?
- Older adults with subclinical cognitive decline or heightened stress
- Individuals seeking cognitive peptide therapy with a preference for non-stimulant, non-sedative options
- Patients with early-stage neurodegenerative changes exploring adjunctive interventions
Note: It is not an approved treatment for dementia or Alzheimer’s disease. Its use should be limited to research settings or closely monitored off-label scenarios. Personalized assessment is critical.
Compounds for Cognitive Health: How Does Selank Compare?
Compared to conventional agents (e.g., cholinesterase inhibitors, benzodiazepines), Selank offers a unique profile combining mild cognitive enhancement and anxiolysis with minimal side effects. Other novel compounds and supplements, such as Rhodiola rosea for endurance and focus and PQQ for mitochondrial support, are being studied for cognitive support, but each has distinct mechanisms and evidence bases.
Individual Variability and Optimizing Outcomes
Response to Selank varies based on genetics, age, baseline cognitive function, and the presence of other neurological or psychiatric diseases. Factors influencing individual outcomes:
- Genetic polymorphisms affecting neuropeptide metabolism
- Baseline neuroinflammatory status
- Co-existing medication regimens
For optimal results:
- Collaborate with a health professional familiar with peptide therapy
- Start with a conservative dosing schedule
- Monitor cognitive and psychological response over 4–8 weeks
Controversies and Research Limitations
While preliminary results are encouraging, Selank faces several obstacles before widespread clinical adoption:
- Lack of large, multinational RCTs: Most studies are small-scale and regionally confined
- Regulatory uncertainty: Outside of select countries, it is not an approved drug and is available as a research compound
- Standardization issues: Variability in peptide synthesis and nasal formulation may influence outcomes
Emerging Directions: Selank and Neurodegenerative Disease
Early-stage research suggests Selank could augment therapy for mild cognitive impairment, age-related cognitive decline, and other neuroinflammatory states. Potential areas of interest include:
- Prevention of stress-induced exacerbation of cognitive decline
- Adjunctive use in multi-modal cognitive therapy programs
- Investigation alongside conventional and emerging cognitive agents
Key Takeaways
- Selank is a promising peptide with low side effects and a unique dual mechanism, targeting both cognitive and anxiety-related symptoms in older adults.
- Its utility is currently supported by modest, primarily regional human evidence, warranting cautious optimism.
- Personalized assessment, expert supervision, and ongoing monitoring are essential until larger-scale data are available.
- Further research, including robust multinational clinical trials, is critical before it can be widely recommended for age-related cognitive decline or neurodegenerative diseases.
Studies / References
- Selank in Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) vs Benzodiazepine
A clinical study of 62 patients with generalized anxiety disorder and neurasthenia compared intranasal Selank with medazepam (a benzodiazepine). Both reduced anxiety symptoms, but it also showed antiasthenic (reduced fatigue) and psychostimulant effects without sedation or dependence, supporting its anxiolytic action in humans.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18454096/ - Selank’s Action on Neurotransmission Gene Expression
Clinical and preclinical research demonstrates that it influences the expression of genes involved in GABAergic neurotransmission and other neural pathways. This molecular activity supports both anxiolytic and potential nootropic effects by modulating inhibitory signaling in the brain.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4757669/ - Clinical Evidence Supporting Anxiolytic and Cognitive Benefits
Selank has been investigated in controlled human studies documenting significant anxiety reduction with minimal side effects and no cognitive impairment — contrasting it with traditional anxiolytics that cause sedation or dependence. These outcomes align with its use in Russian clinical practice. - Selank’s Development and Pharmacology (Nootropic/Anxiolytic Peptide)
It is a synthetic heptapeptide derived from tuftsin, developed to modulate neurotransmitter systems including serotonin, dopamine, and GABA — mechanisms linked with both mood regulation and cognitive stability in clinical contexts.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Selank - Reported Human Clinical Effects & Cognitive Links
Reviews of clinical use highlight effects on anxiety scores and associated improvements in emotional stability and cognitive performance measures — though much of this data comes from Russian trials not yet replicated in Western RCTs.
Conclusion
Selank offers a novel approach to supporting cognitive health in aging, combining anxiolytic and neuroprotective mechanisms with a strong safety profile. While it is not a cure-all, and human data remain limited, its potential as a cognitive peptide therapy continues to drive research in neuroprotection and the management of age-related decline. Individuals interested in it should proceed under medical supervision and in the context of ongoing clinical evaluation.