As the human body ages, its innate repair and regeneration capabilities gradually decline. This biological slowdown is linked to a reduction in certain signaling molecules that orchestrate cellular health. Among the most researched of these molecules is GHK-Cu, a naturally occurring copper peptide that has garnered significant attention for its potential to rejuvenate tissues, from the skin to internal systems. Its discovery decades ago opened a new chapter in understanding how the body maintains and repairs itself, and modern research continues to uncover its multifaceted roles.
This article provides an expert, evidence-based exploration of GHK-Cu. We will delve into its mechanism of action, review the human clinical evidence supporting its benefits, discuss practical administration methods and dosages, and outline the critical safety considerations. While the promise of reversing age-related decline is compelling, a cautious and informed approach is essential, grounding any potential application in solid scientific understanding.
What is GHK-Cu and How Does It Work?
GHK-Cu is a tripeptide, meaning it consists of three amino acids—glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine—with a strong affinity for binding to copper ions (Cu2+). It was first isolated from human plasma in 1973 by Dr. Loren Pickart, who observed that it had the remarkable ability to make old liver cells behave like younger ones. This foundational discovery highlighted GHK’s role as a key regulator of cellular health, a function that diminishes as its concentration in the body naturally falls with age. By age 60, the levels of GHK in the plasma drop by as much as 60% from the levels in our twenties.
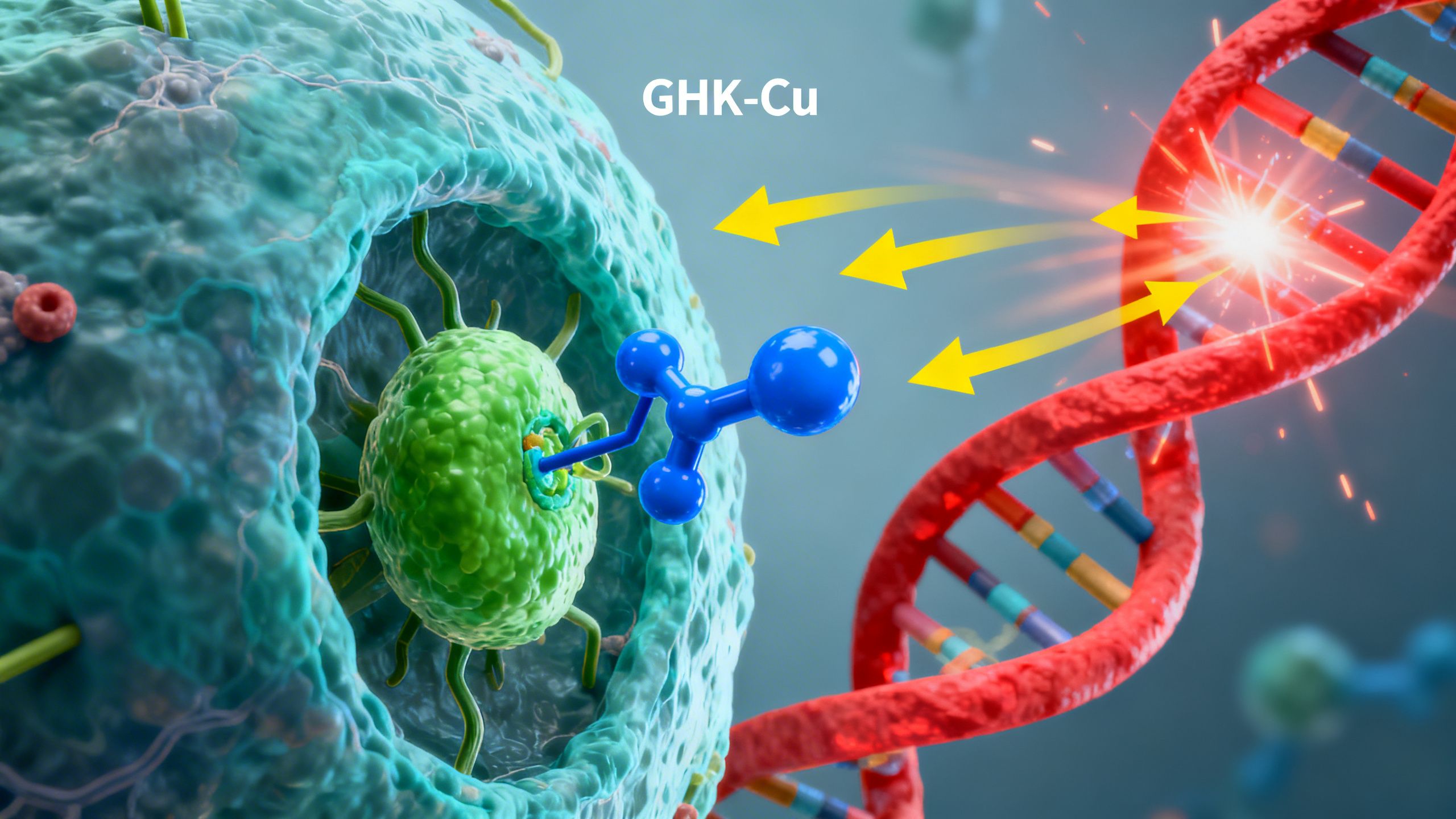
The primary mechanism of action for GHK-Cu is its profound influence on gene expression. Research has shown that GHK can modulate the activity of thousands of human genes, essentially resetting them to a younger, healthier state. It upregulates genes involved in antioxidant defense, tissue repair, and anti-inflammatory pathways while downregulating genes associated with inflammation and tissue destruction. This genetic reset is the cornerstone of its wide-ranging biological effects.
Beyond gene modulation, GHK-Cu exerts its influence through several other critical pathways:
- Stimulation of Extracellular Matrix Proteins: GHK-Cu is a potent stimulator of collagen, elastin, glycosaminoglycans, and proteoglycans. These structural proteins are essential for the integrity, firmness, and elasticity of the skin and connective tissues. By boosting their synthesis, GHK-Cu helps rebuild and strengthen the tissue framework.
- Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Action: The peptide exhibits powerful anti-inflammatory properties by reducing the levels of key inflammatory cytokines like IL-6. It also acts as a potent antioxidant, protecting cells from the damaging effects of free radicals and oxidative stress, which are major drivers of aging and disease.
- Promotion of Angiogenesis: GHK-Cu promotes the formation of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis. This is crucial for wound healing and tissue regeneration, as a robust blood supply is necessary to deliver oxygen and nutrients to damaged areas.
- Support for Stem Cell Function: Emerging research suggests that GHK-Cu helps maintain the health and proliferative potential of stem cells. By creating a healthier, more youthful microenvironment, it supports the body’s endogenous stem cell population, which is vital for long-term repair and maintenance.
Human Evidence for GHK-Cu Peptide Benefits
While much of the initial research on GHK-Cu was conducted in vitro or in animal models, a growing body of human clinical trials has validated its efficacy, particularly in dermatology and wound care. It’s crucial to focus on this human evidence to understand its practical applications.
Skin Health and Anti-Aging
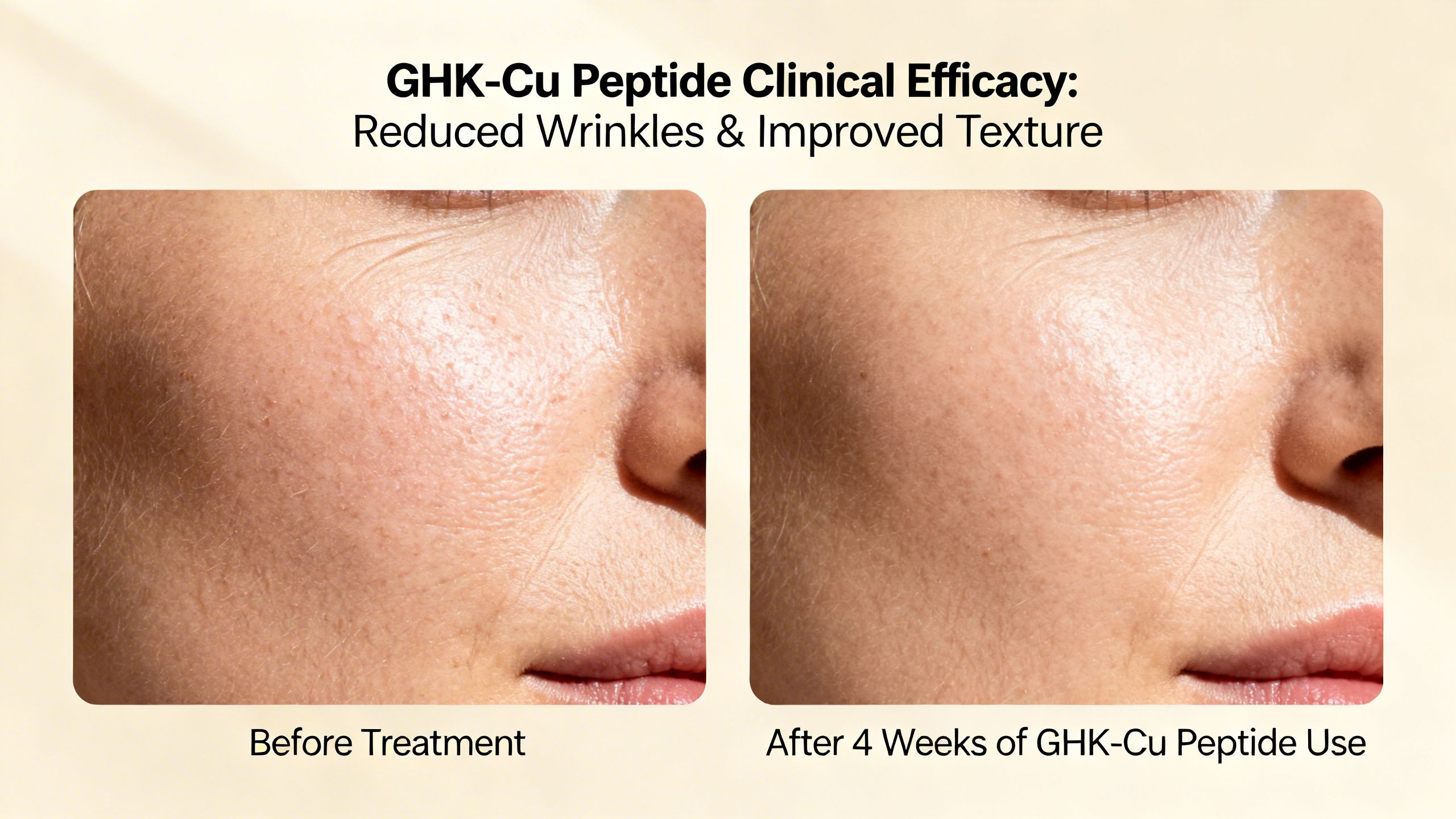
The most extensive human research on GHK-Cu is in the field of cosmetic dermatology. Its ability to rebuild the dermal matrix makes it a popular ingredient in high-end anti-aging products. Multiple clinical studies have demonstrated tangible GHK-Cu peptide benefits for photoaged skin.
In one notable 12-week study involving 71 women with mild to advanced signs of photoaging, a facial cream containing GHK-Cu was compared against creams containing vitamin C and retinoic acid. The results showed that the GHK-Cu group experienced significant improvements in skin laxity, clarity, and firmness, and a reduction in the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. The peptide was found to be non-irritating and more effective than vitamin C and retinoic acid in increasing collagen production.
Another study focused on eye creams with GHK-Cu. After 12 weeks of application, participants showed a significant reduction in the depth of crow’s feet wrinkles and an increase in skin density and thickness compared to a placebo. These “GHK-Cu before and after” results are attributed to the peptide’s ability to penetrate the stratum corneum and signal for dermal repair.
Wound Healing and Tissue Repair
GHK-Cu’s foundational role is in tissue remodeling and repair. Its application in wound care is supported by human studies demonstrating its ability to accelerate healing. By promoting angiogenesis, reducing inflammation, and stimulating the synthesis of repair proteins, it creates an optimal environment for tissue closure.
Human trials have shown that topical application of GHK-Cu can improve the healing of chronic wounds, such as diabetic ulcers and pressure sores, which are notoriously difficult to treat. In these settings, the peptide helps to clear damaged proteins and cellular debris while laying down a new, healthy extracellular matrix. Its ability to improve outcomes in compromised healing situations makes it an area of active medical research.
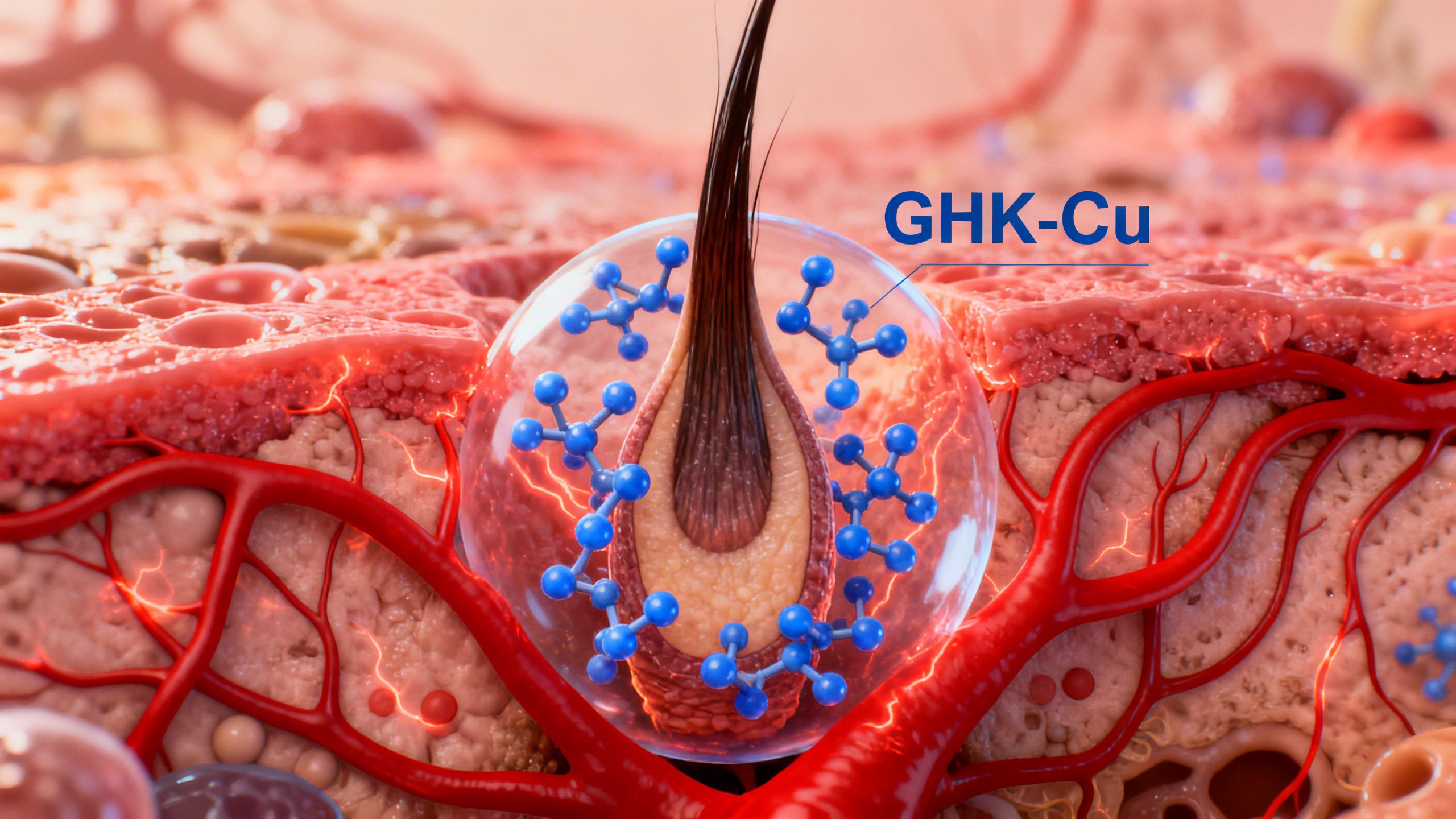
Hair Growth Stimulation
Androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness) is characterized by the miniaturization of hair follicles. GHK-Cu has shown promise in counteracting this process. The mechanism is believed to involve increasing the size of the hair follicle and prolonging the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle.
One human study compared the efficacy of a GHK-Cu-containing scalp product to a product containing 5% minoxidil, a well-known hair growth stimulant. The study found that the GHK-Cu complex was similarly effective in stimulating hair growth and increasing follicle size. It works by improving vascularity in the scalp, delivering more nutrients to the follicle, and stimulating the production of key structural proteins necessary for healthy hair.
Systemic and Neuroprotective Potential
While most human data pertains to topical use, there is growing interest in the systemic effects of injectable GHK-Cu. Animal studies suggest it may have protective effects on various organs, including the lungs, liver, and nervous system. It has been shown to suppress inflammation, protect against oxidative damage, and even promote nerve outgrowth.
However, it is critically important to note that human data on systemic or neuroprotective effects is extremely limited. The translation of these findings from animal models to human clinical practice is still in its infancy. Claims of cognitive enhancement, systemic anti-aging, or disease prevention from injectable GHK-Cu are largely speculative at this stage and require rigorous human trials for validation.
GHK-Cu Dosage and Methods of Administration
The method of administration and the appropriate GHK-Cu dosage depend entirely on the intended goal. The vast majority of established use is topical, while injectable forms are considered experimental.
Topical Application (GHK-Cu Cream and Serums)
For skin rejuvenation and hair growth, topical application is the standard. GHK-Cu is incorporated into creams, lotions, and serums at concentrations typically ranging from 1% to 3%.
- For Facial Skin: Products are usually applied once or twice daily to clean skin. The peptide’s small size allows for some penetration into the epidermis and dermis to exert its effects.
- For Hair: Scalp serums or foams are applied directly to the areas of thinning hair. Consistent, long-term use (3-6 months) is generally required to see noticeable results.
Topical application is highly effective for localized benefits and is associated with an excellent safety profile.
Subcutaneous Injections
Injectable GHK-Cu is used for its potential systemic effects, such as accelerated recovery from injury, reduced systemic inflammation, or widespread tissue repair. This method delivers the peptide directly into the bloodstream, allowing for distribution throughout the body.
Disclaimer: The following information is for educational purposes only and is based on research protocols. It is not medical advice. Self-administering injectable compounds without medical supervision carries significant risks, including infection, incorrect dosing, and adverse reactions. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional to discuss appropriate treatment options.
In research settings, the typical GHK-Cu peptide injection dosage ranges from 1 to 2 milligrams per day, administered via subcutaneous injection (into the fatty tissue under the skin). These injections are often performed in cycles, such as 5 days on, 2 days off, or for a duration of 30-60 days, followed by a break.
It’s important to distinguish between GHK and GHK-Cu for injection. Most often, the peptide is sold as GHK (without copper), which is then reconstituted with bacteriostatic water. Upon injection, the GHK peptide readily binds with the abundant copper ions available in the bloodstream and tissues to become active GHK-Cu.
Microneedling
To enhance the penetration of topical GHK-Cu, it is sometimes used in conjunction with microneedling. This procedure creates micro-channels in the skin, allowing the peptide to reach the deeper layers of the dermis more effectively. This combination can amplify the collagen-stimulating and skin-rejuvenating effects of the peptide.
Safety, Risks, and GHK-Cu Side Effects
Overall, GHK-Cu is considered to have a high safety profile, especially when used topically. However, the potential for side effects varies with the method of administration.
Topical Side Effects
When applied to the skin as a GHK-Cu cream or serum, side effects are rare and typically mild. They may include:
- Minor skin irritation
- Redness
- Itching
These effects are more likely at higher concentrations and usually resolve on their own. As with any new skincare product, a patch test is recommended before widespread use.
Injectable GHK-Cu Side Effects
Systemic administration via injection carries a different and more significant set of potential risks. GHK-Cu side effects from injections can include:
- Injection Site Reactions: Pain, redness, swelling, or itching at the injection site are common.
- Systemic Effects: Some users report transient feelings of nausea, headache, dizziness, or flushing shortly after injection. These effects are usually mild and short-lived.
- Copper Dysregulation: This is a theoretical but serious concern. GHK-Cu is a copper carrier and regulator. However, excessive, long-term dosing could potentially disrupt the body’s delicate copper homeostasis. Copper is a heavy metal that can be toxic in high amounts. Therefore, adhering to established dosage protocols and taking breaks is crucial.
Individuals with copper metabolism disorders, such as Wilson’s disease, should absolutely avoid GHK-Cu supplementation. Due to these risks, injectable use should only be considered under the guidance of a knowledgeable medical professional who can monitor for potential adverse effects.

Studies / References
Below is a summary of several key human studies that form the evidence base for GHK-Cu’s effects.
1. GHK-Cu & Human Tissue Remodeling / Skin Repair (Review)
GHK (and its copper complex GHK-Cu) is a naturally occurring peptide that promotes tissue remodeling, accelerates wound healing, and has anti-inflammatory actions. Although human clinical evidence for some effects is limited, its role in skin regeneration has been demonstrated.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18644225/
2. Mechanistic Evidence for GHK-Cu’s Biological Actions
The peptide stimulates blood vessel and nerve outgrowth, increases collagen/elastin synthesis, supports fibroblast activity, and influences gene regulation related to tissue repair and aging processes.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29986520/
3. Topical GHK-Cu Improves Skin Structure (Clinical Skin Aging Outcome)
In a randomized, double-blind clinical trial, topical application of a GHK-Cu peptide formulation demonstrated significant improvement in wrinkle volume reduction and skin remodeling compared with control.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6073405/
4. Anti-Inflammatory & Antioxidant Mechanisms (Preclinical Evidence)
GHK-Cu exhibits antioxidant activity, modulates inflammatory markers, and protects cells from oxidative damage — mechanisms relevant to inflammation and aging science.
https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/5/2/29
5. GHK-Cu Decline with Age & Aging Peptide Potential
Plasma levels of GHK decline with age, and the peptide has demonstrated tissue repair, anti-inflammatory, and anti-aging potential in cell and animal studies, providing rationale for ongoing clinical research.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8789089/
Conclusion
GHK-Cu stands out as one of the most well-researched regenerative peptides available today. Its fundamental role in modulating gene expression to promote repair and reduce inflammation provides a strong scientific basis for its observed benefits. The human clinical evidence is robust for its use in cosmetic applications, where it has been proven to improve skin health, reduce signs of aging, and stimulate hair growth with an excellent safety profile.
Its potential extends to more medical applications, such as accelerating the healing of chronic wounds. However, the excitement surrounding its potential systemic, anti-aging, and neuroprotective benefits from injectable use must be tempered with caution. This area remains largely experimental, and the long-term safety and efficacy in humans have not yet been established through large-scale clinical trials. As with any powerful biological compound, a responsible approach grounded in evidence and guided by professional medical advice is paramount to safely harnessing the regenerative potential of GHK-Cu.


