Mitochondria, often called the cell’s “powerhouses,” are central to energy production and play a critical role in the health and longevity of both our muscles and brains. As we age, maintaining mitochondrial function becomes vital in preserving muscle strength, preventing cognitive decline, and supporting overall vitality. Recent research highlights a suite of mitochondrial nutrients—including both classic compounds and cutting-edge peptides—that may offer powerful support for muscle and brain health.
This article provides a comprehensive, evidence-based overview of three key mitochondrial nutrients: MOTS-c, Epitalon, and CoQ10. We will explore how these compounds work, survey the human research, discuss their safety, and consider how they may help counteract the effects of mitochondrial dysfunction seen in aging, sarcopenia, and neurodegeneration.
Understanding Mitochondrial Health in Aging
The Role of Mitochondria in Muscle and Brain Function
Mitochondria generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the universal “fuel” for cellular processes. Healthy mitochondria are particularly essential in tissues with high energy demands, such as skeletal muscle and the brain.
- In muscles: Mitochondria power contraction, endurance, and repair. Reduced mitochondrial efficiency is linked to muscle atrophy (sarcopenia) and frailty.
- In the brain: Mitochondria support neuronal function, protect against oxidative stress, and help regulate memory and cognition. Dysfunction is associated with neurodegenerative diseases and age-related cognitive decline.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Degeneration
Research suggests that aging is accompanied by a decline in both mitochondrial quantity and quality. This contributes to loss of muscle mass, decreased strength, slower recovery from exercise or injury, and cognitive issues ranging from brain fog to dementia.
1. MOTS-c: A Novel Peptide for Mitochondrial Health
What is MOTS-c?
MOTS-c (mitochondrial open reading frame of the 12S rRNA-c) is a newly identified mitochondrial-derived peptide (MDP). Unlike most proteins encoded by nuclear DNA, MOTS-c is encoded within the mitochondrial genome. It acts as a cellular metabolic regulator with promising implications for both muscle and brain health.
Mechanisms of Action
- Enhances mitochondrial biogenesis: MOTS-c stimulates production of new mitochondria, especially in muscle tissue
- Promotes glucose utilization: It helps regulate insulin sensitivity and supports healthy blood sugar management
- Protects against oxidative stress: MOTS-c activates antioxidant defenses, reducing cellular damage
- Supports exercise performance and recovery
Human Evidence for Muscle and Brain Benefits
Human studies have linked higher MOTS-c levels to improved muscle function in older adults and protection against metabolic syndrome. Some trials indicate better endurance, reduced inflammation, and healthy body composition.
Caveat: Most clinical data is preliminary. Larger, longer-term studies are ongoing.
Safety and Individual Variability
MOTS-c appears safe in early studies. However, there is a lack of long-term safety data, especially in populations with specific health conditions. Genetic variability may influence individual responses.
2. Epitalon: A Peptide Linked to Longevity and Neuromuscular Support
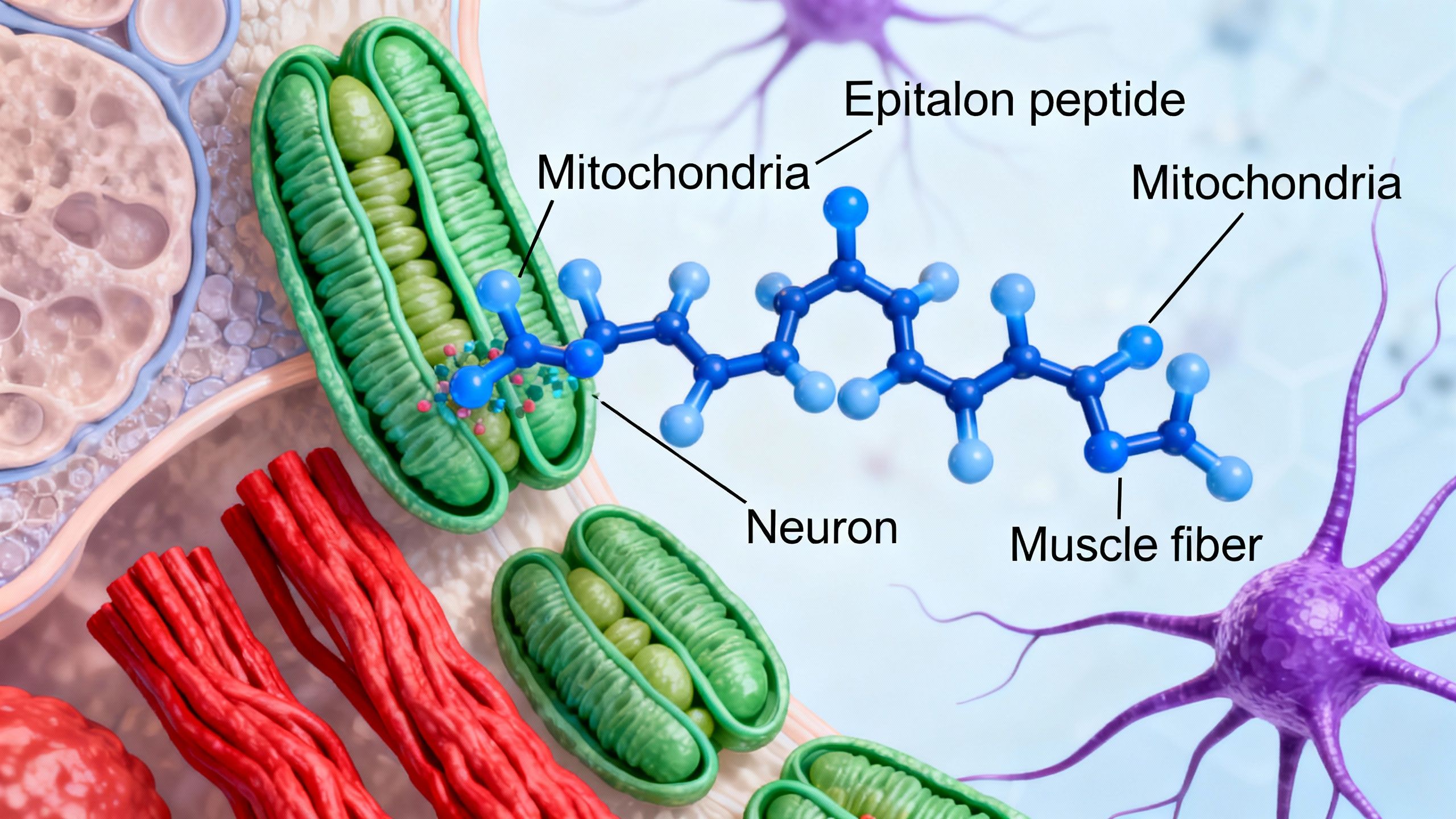
What is Epitalon?
Epitalon (also called epithalamin or epithalon) is a synthetic peptide derived from the pineal gland protein epithalamin. This peptide has garnered attention for its potential to modulate aging processes, partly by influencing mitochondrial function.
Mechanisms of Action
- Stimulates telomerase activity: May slow cellular aging by preserving telomere length
- Normalizes circadian rhythm: Supports healthy sleep-wake cycles, beneficial for brain health
- Reduces oxidative stress: Acts as a mitochondrial antioxidant
- Promotes cellular repair and neuroprotection
Human Evidence for Longevity and Function
Studies in older adults indicate improved sleep quality, mood, and physical endurance after Epitalon use. Some data suggest enhanced cognitive function and reduced markers of biological aging.
Caveat: Most published research comes from Eastern Europe, with limited availability of large, double-blind Western clinical trials.
Safety Profile
Epitalon has shown few adverse effects in controlled settings. However, access and regulation vary, and high-quality evidence on long-term or higher-dose usage remains limited.
3. CoQ10: The Classic Mitochondrial Nutrient

What is CoQ10?
Coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinone) is a vitamin-like compound found in every cell and concentrated in mitochondria. It’s essential for producing ATP during cellular respiration and also functions as a potent antioxidant.
Mechanisms of Action
- Facilitates electron transport: Core component for ATP production
- Neutralizes free radicals: Protects cells from oxidative damage
- Supports cardiovascular, muscular, and neurological function
Human Evidence for Muscle, Brain, and Aging
Multiple clinical trials demonstrate that CoQ10 can:
- Improve exercise performance and reduce fatigue in older and athletic populations
- Support cognitive function in aging individuals and those at risk of neurodegenerative disease
- Decrease muscle pain and weakness associated with statin medications
Limitations: Benefits may depend on baseline CoQ10 status and formulation (ubiquinol is more bioavailable than ubiquinone).
Safety and Dosage
CoQ10 has an excellent safety record in human studies. Side effects are generally mild (e.g., digestive upset). Doses range from 100 to 400 mg/day, but individual responses can vary.
Mechanistic Comparison: How These Mitochondrial Nutrients Work
| Nutrient | Primary Mechanism | Human Evidence | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOTS-c | Mitochondrial biogenesis | Emerging, promising | Improves muscle function, metabolism |
| Epitalon | Telomere maintenance | Modest, preliminary | Supports sleep, mood, cellular aging |
| CoQ10 | Electron transport/antiox | Robust, established | Energy, muscle, cognitive support |
Integrating Mitochondrial Nutrients into Everyday Life
Who May Benefit?
- Aging adults seeking to maintain muscle mass and brain function
- Individuals with documented mitochondrial dysfunction
- Athletes looking to optimize recovery and endurance
- Those with chronic health conditions affecting energy metabolism
Practical Guidelines
- Consult a physician: Especially if considering peptide therapies or high-dose supplementation
- Focus on lifestyle first: Physical activity, resistance training, sleep, and a nutrient-rich diet remain foundational for mitochondrial health
- Consistency matters: Mitochondrial support compounds work best over weeks to months, not days
Individual Variability
Genetics, pre-existing conditions, diet, and lifestyle play major roles in how mitochondrial nutrients affect each person. Monitoring response and discussing with a healthcare provider is crucial.
Safety, Interactions, and Medical Cautions
- MOTS-c and Epitalon: Though generally well tolerated, peptides are not regulated as dietary supplements in many countries. Medical supervision is advised.
- CoQ10: Can interact with some blood thinners and blood pressure medications; discuss with your prescriber before use.
- Comprehensive management: For diagnosed mitochondrial diseases, nutrient interventions should supplement—not replace—conventional care.
Always seek qualified medical advice before starting new interventions, particularly for complex health conditions.
Studies / References
- MOTS-c: Biological Role in Aging and Metabolic Regulation
A comprehensive review article describes MOTS-c as a mitochondrial-derived peptide that regulates metabolism and may have beneficial effects in age-related diseases by influencing cellular stress responses and metabolic pathways.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36233287/ - Epitalon Induces Telomerase Activity and Telomere Extension in Human Cells
In cultured human somatic cells, Epitalon significantly increased telomerase activity and telomere length, indicating a potential mechanism for supporting cellular aging processes (in vitro human cell study).
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40908429/ - Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation for Statin-Induced Muscle Symptoms
A clinical trial protocol investigating whether CoQ10 supplementation helps reduce statin-associated muscle aches, weakness, and fatigue. (This study is registered and shows ongoing clinical human research on muscle support with CoQ10.)
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01032993 - Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation and Statin-Associated Myopathy (Meta-Analysis)
A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials found that CoQ10 supplementation significantly reduced muscle pain intensity in patients with statin-associated muscle symptoms, suggesting mitochondrial support benefits in this context.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/PMC12554813/ - CoQ10 Supports Mitochondrial Function in Aging and Disease
A review highlights that CoQ10 is essential for mitochondrial electron transport and may alleviate oxidative stress and symptoms related to ageing and age-associated mitochondrial deficiency, though more long-term human research is needed.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0047637421000932
Conclusion: The Future of Mitochondrial Nutrients for Muscle and Brain Health
Emerging and established mitochondrial nutrients—including MOTS-c, Epitalon, and CoQ10—offer real promise for supporting muscle and brain health as we age. While classic nutrients like CoQ10 are backed by decades of research, new peptides such as MOTS-c and Epitalon are quickly moving from research labs into clinical consideration.
Maintaining mitochondrial function may be key to resisting sarcopenia, preserving cognitive ability, and enhancing healthy aging. As evidence grows, tailored interventions using mitochondrial nutrients for muscle and brain health are becoming an exciting frontier in medicine.
Discuss these options with your healthcare provider, and remember: nutrient therapy is most effective when combined with lifestyle approaches and medical guidance.