Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a critical compound for cellular energy production and acts as a potent antioxidant in the human body. Its relevance to aging, cellular metabolism, and overall health has been the focus of intense clinical interest. As we age, the role of it becomes even more vital, with studies exploring its potential to support mitochondrial function, maintain cardiovascular health, and protect against age-associated cellular stress. This article provides a comprehensive, evidence-based overview of CoQ10, unpacking its human research, mechanisms of action, benefits, and safety considerations.
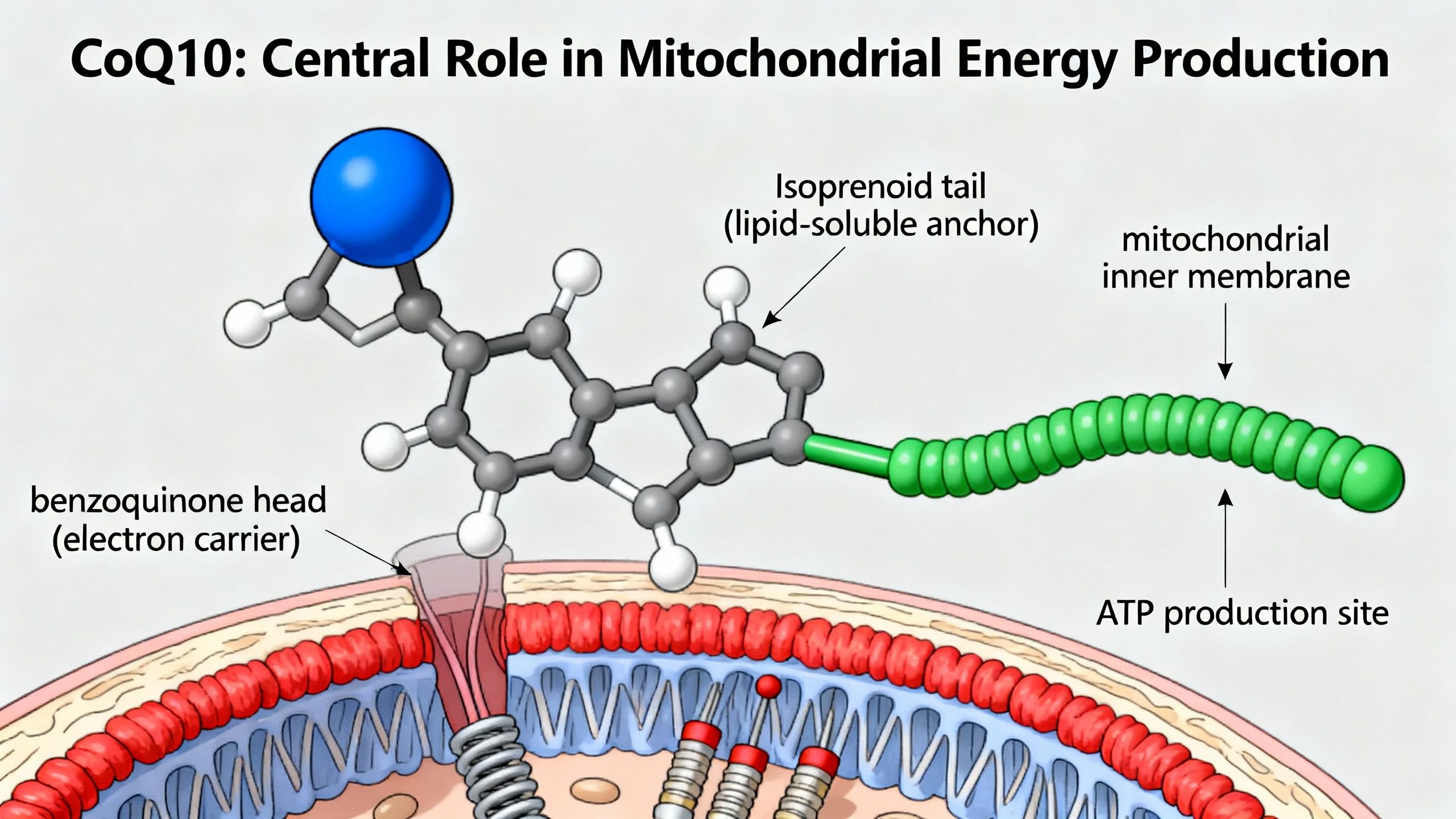
What Is CoQ10? An Introduction to Its Essential Role
CoQ10, short for coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinone/ubiquinol), is a fat-soluble compound naturally found in all human cells, with the highest concentrations in organs that demand substantial energy, such as the heart, liver, and kidneys. It is integral to the mitochondrial electron transport chain, catalyzing the conversion of nutrients into cellular energy (adenosine triphosphate, ATP).
Key Facts:
- Naturally produced but levels decline with age and certain diseases
- Exists in two forms: ubiquinone (oxidized) and ubiquinol (reduced, active antioxidant form)
- Sourced from foods (especially oily fish, meat, nuts) and supplements
The Role in Healthy Aging
As humans age, Q10 synthesis decreases, reducing cellular energy production and increasing vulnerability to oxidative stress. These changes are hypothesized to contribute to common signs of aging, including reduced muscle function, cognitive decline, and increased cardiovascular risk.

How CoQ10 Supports Mitochondrial Energy Production
CoQ10 functions as an essential electron carrier within the mitochondrial respiratory chain. It shuttles electrons between complexes I/II and complex III, playing a pivotal part in generating ATP. Without adequate Q10, ATP production is impaired, resulting in cellular energy deficits—this is especially problematic in tissues with high energy needs.
Mechanisms in Mitochondrial Metabolism
- Acts as an electron transporter for ATP synthesis
- Supports mitochondrial membrane stability
- Scavenges free radicals, limiting mitochondrial DNA damage
Clinical significance: Impaired mitochondrial function is a hallmark of aging. Maintaining Q10 may support overall metabolic health, muscle vitality, and cognitive performance as we age.
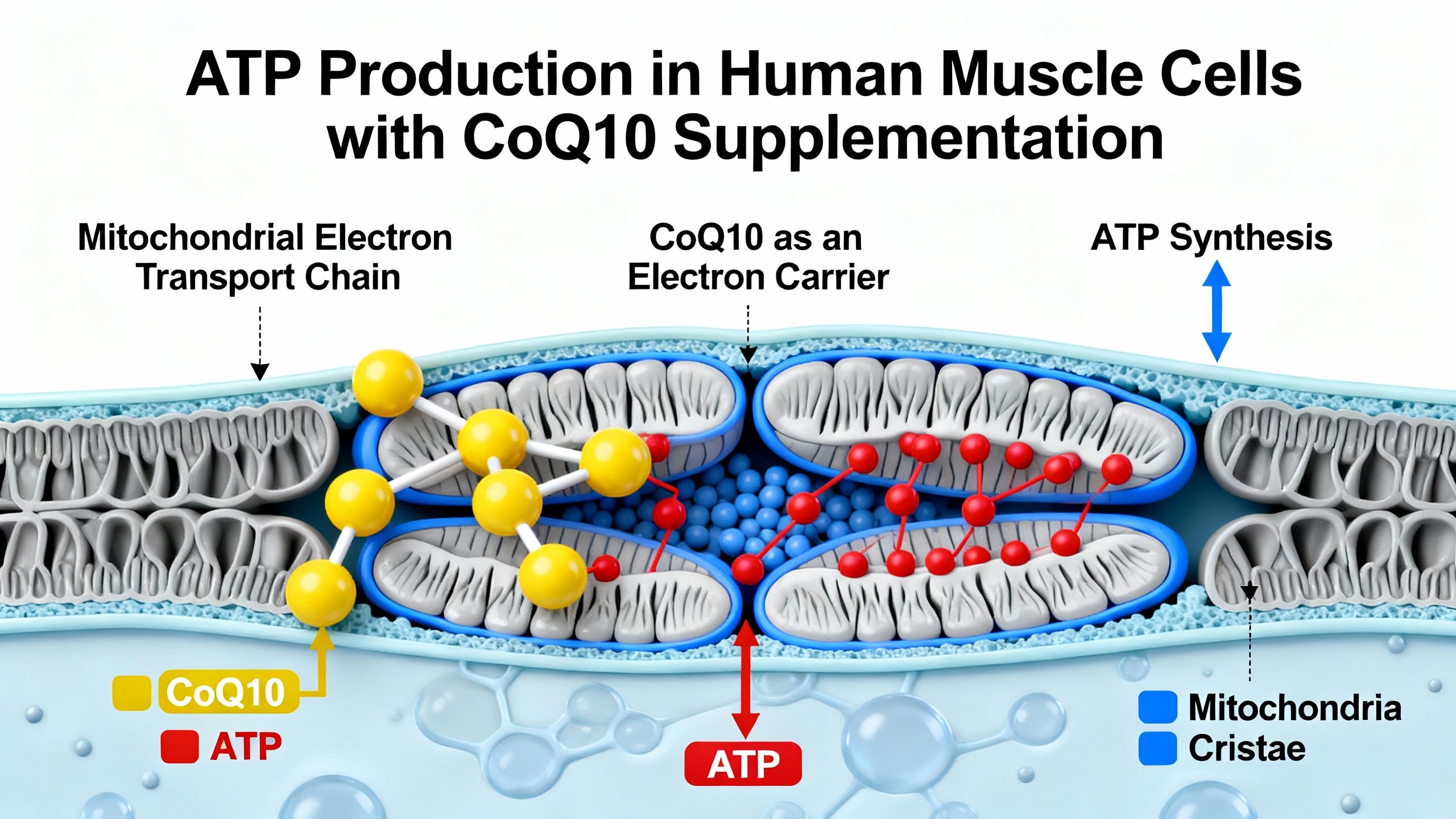
The Link Between CoQ10 and Oxidative Stress in Aging
Oxidative stress arises from an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, leading to cellular damage and inflammation. It is one of the body’s most powerful fat-soluble antioxidants, protecting cell membranes and mitochondrial DNA from oxidative attacks.
Evidence for Antioxidant Protection:
- Reduces lipid peroxidation in cellular membranes
- Regenerates other antioxidants like vitamin E
- Clinical studies link higher CoQ10 status to lower biomarkers of oxidative damage in older adults
Daily Q10 supplementation has been shown to decrease markers of oxidative stress, particularly in populations with chronic conditions or advancing age.

7 Evidence-Based Benefits of CoQ10 for Healthy Aging
1. Enhanced Cellular Energy and Physical Function
Human trials consistently demonstrate that CoQ10 supplementation boosts levels in muscle tissue and plasma, particularly in older adults. Improved muscle energy correlates with increased exercise capacity and reduced fatigue in both healthy seniors and those with chronic disease.
2. Cardiovascular Health Support
It is well-studied in the context of cardiovascular aging. Supplementation has shown benefits for:
- Blood pressure regulation (notably in hypertensive adults)
- Symptoms of heart failure (when taken alongside standard medications)
- Reducing oxidative stress in vascular tissue
3. Cognitive Function and Brain Aging
Cognitive decline is partially linked to mitochondrial dysfunction. Human studies find that CoQ10 supplementation can improve markers of attention, memory, and mental fatigue in older adults, though findings are most robust for those with mild cognitive impairment or neurological risk factors.
4. Mitigating Statin-Induced Muscle Symptoms
Statins, commonly used for cholesterol reduction, may reduce endogenous CoQ10. Clinical trials indicate that supplementation may help reduce statin-associated muscle pain and weakness in susceptible individuals.
5. Skin Aging and Photoprotection
Topical and oral CoQ10 regimens have demonstrated improvements in skin elasticity and reduction in visible signs of aging. Human studies attribute this to increased antioxidant defense in the skin and improved collagen structure.
6. Fertility Enhancement in Aging Populations
There is encouraging evidence that CoQ10 supplementation improves ovarian function in women over 35 years, and enhances sperm quality in males with age-related fertility concerns.
7. Immune System Support
Preliminary human data show that older adults taking it may experience better immune cell activity and resilience during periods of increased oxidative stress, including recovery from strenuous physical activity or illness.
Exploring Dosage, Forms, and Bioavailability
- Typical Dosage Range: 100–300 mg per day for adults (clinical studies)
- Bioavailability Tips: Ubiquinol is more readily absorbed than ubiquinone in older adults
- Absorption is improved when taken with meals containing fat
CoQ10 is available as both over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription formulations in some regions. A healthcare professional should be consulted for personalized advice, especially when combining it with other medications.
Safety Considerations and Known Interactions
CoQ10 is generally well-tolerated in human studies, even at doses up to 1200 mg/day, but some individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal upset (nausea, diarrhea, appetite loss).
Important interactions and caveats:
- May lower blood pressure, necessitating doctor supervision in individuals on anti-hypertensive medication
- Can alter the action of certain anticoagulant drugs (e.g., warfarin)
- Should be used cautiously alongside chemotherapy due to possible drug interactions affecting efficacy
CoQ10 Supplementation in Older Adults: Practical Applications
Given diminishing endogenous CoQ10 with age, supplementation may be most beneficial for:
- Adults over age 50
- Individuals with cardiovascular or metabolic conditions
- Those experiencing statin-related side effects
- People looking for adjunctive support for healthy cognitive aging
A personalized approach is always best. Speak to your healthcare provider to determine if it fits your regimen, especially if you take chronic medications or have complex medical conditions.
Studies / References: Human Evidence at a Glance
1. Cardiovascular Support in Older Adults
Clinical trials have investigated CoQ10 supplementation in adults with chronic heart failure. In long-term studies (100 mg three times daily for up to 2 years), participants showed a reduction in major cardiovascular events and mortality, particularly those with lower baseline CoQ10 levels. While promising, the evidence comes from limited populations, so broader conclusions require further validation.
Reference: Mortensen et al., Q-SYMBIO Trial, 2014
2. Cognitive Function in Seniors
Research exploring cognitive performance suggests that CoQ10 may help improve memory, attention, and executive function in older adults with mild cognitive difficulties. A 6-month trial using 200 mg/day demonstrated improvements in select cognitive markers, although participants with normal cognition did not show significant changes. These findings indicate potential benefits, but results remain preliminary.
Reference: Coenzyme Q10 and Cognition Review
3. Statin-Associated Muscle Symptoms
Statin medications can reduce natural CoQ10 levels, potentially contributing to muscle pain or weakness in some users. Small clinical studies suggest that supplementation (100–200 mg/day) may help alleviate these symptoms, though results are mixed depending on the type of statin and baseline muscle discomfort. Larger, well-controlled trials are needed to confirm effectiveness.
References:
4. Skin Aging and Photoprotection
Both oral and topical CoQ10 have been studied for skin health, showing modest improvements in elasticity, smoothness, and fine wrinkles. The compound appears to enhance antioxidant defenses in skin cells, but evidence is currently limited and warrants larger human trials for confirmation.
Reference: CoQ10 and Skin Anti-Aging Effects
5. Male Fertility Enhancement
Several studies indicate that CoQ10 may support sperm quality in men with fertility concerns, particularly improving motility and concentration. Supplementation (commonly 200 mg/day for 6 months) was associated with measurable benefits, although long-term outcomes and pregnancy success rates are less clear.
Reference: Systematic Review: CoQ10 and Male Fertility
Conclusion: Harnessing the Benefits of CoQ10 for Lifelong Vitality
CoQ10 stands out as one of the most rigorously studied compounds supporting healthy aging and optimizing cellular energy. Its antioxidant and mitochondrial roles underpin benefits for the heart, brain, muscles, skin, and reproductive health. Clinical trials suggest that targeted supplementation—ideally tailored to an individual’s age, health, and medication status—can help bridge the gap left by age-related decline in natural CoQ10 production.
For those seeking to support vigorous aging and resilience, CoQ10 represents a practical, science-backed option to discuss with your healthcare provider. Ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of its full potential and optimal application across diverse populations.



